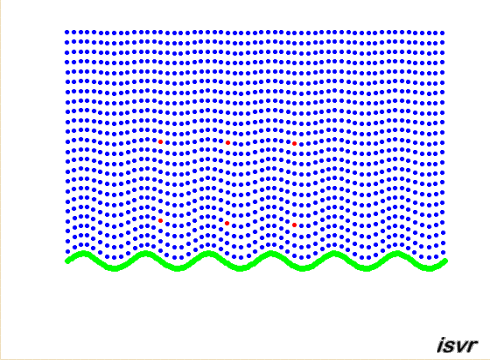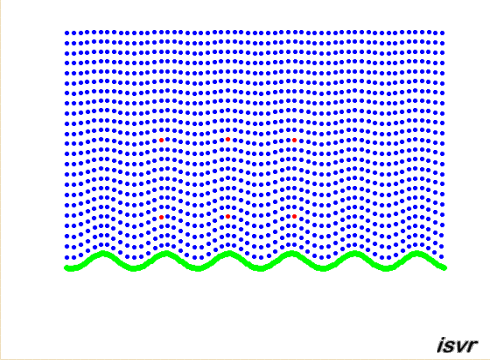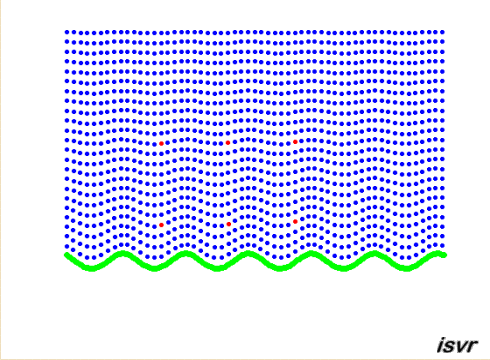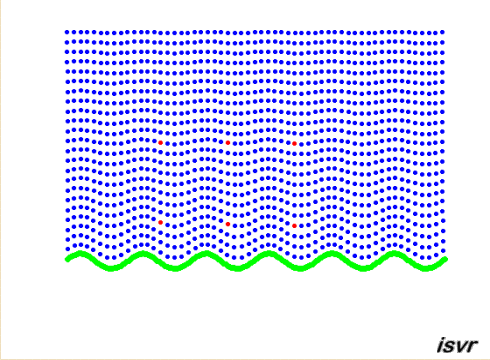
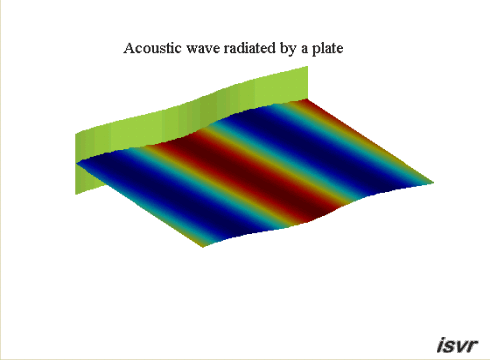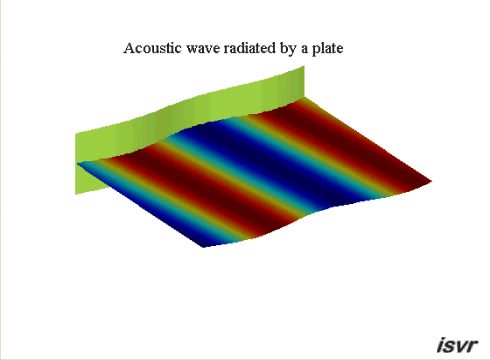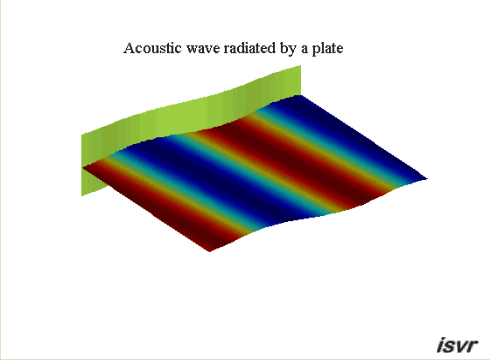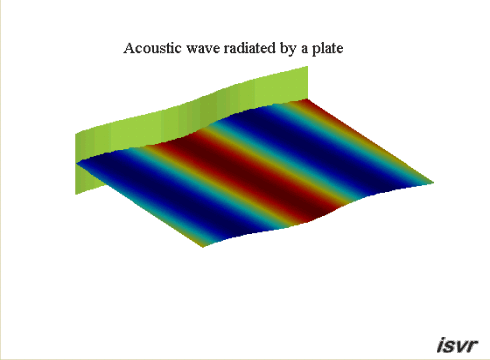
Propagating waves
A vibrating plate in
contact with a fluid at rest may radiate sound by producing
acoustic plane waves that travel away from the plate. In the case of an
infinite plate, this only happens if the wavelength of the bending waves
in the plate is larger than the acoustic wavelength.
This occurs when the travelling wave speed of the plate is higher than the
wave speed in the fluid. This case is illustrated by the animation below:
The animation below shows
the particle displacement induced by a vibrating panel radiating sound in
the fluid medium. By concentrating on the red dots, one can see that the
particles are oscillating back and forth through an equilibrium position.

Evanescent
waves
If the wavelength of the
bending waves in the plate is shorter than the acoustic wavelength, then the
acoustic waves do not propagate into the fluid. We are left with
what are called 'evanescent' waves where the pressure amplitude decreases exponentially with
distance from the plate.
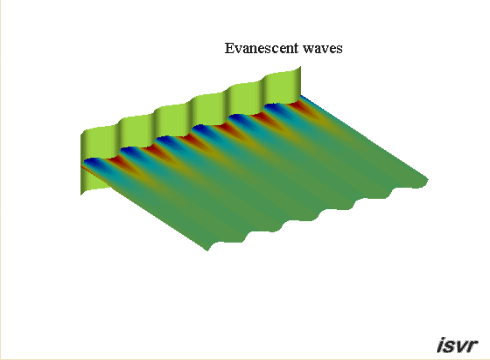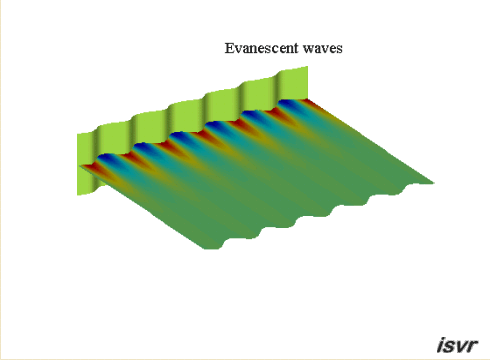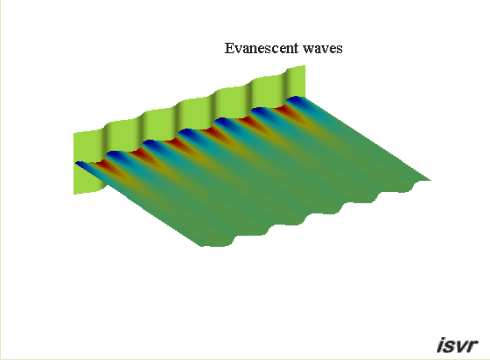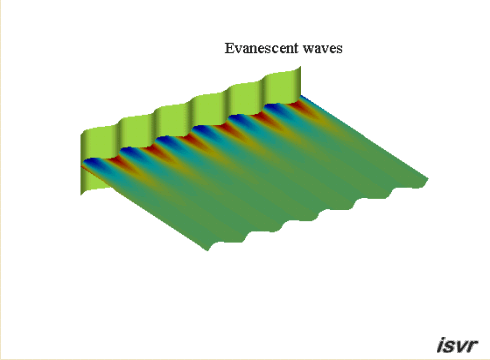
The animation below shows the particle
displacement induced by a vibrating panel when the travelling wave speed
in the panel is less than the wave speed in the fluid. The amplitude of
the particle motion decreases exponentially with increasing distance from
the boundary. By concentrating on the red dots, you can just see that the
particles move in an ellipse.